CHOLINE OXIDASE from Alcaligenes sp.
CHO-301
Choline: oxygen 1-oxidoreductase (EC 1.1.3.17)¹ ˜ ⁷⁾
(CH₃)₃N⁺CH₂CH₂OH + H₂O +2O₂ ► (CH₃)₃N⁺CH₂COO‾ + 2H₂O₂
Choline Betaine
| Appearance: | Yellowish amorphous powder, lyophilized | |
|---|---|---|
| Activity: | GradeIII 10U/mg -solid or more (containing approx. 20% of stabilizers) |
|
| Contaminant: | Catalase ≤1.0×10²% |
|
| Stabilizers: | EDTA, BSA, amino acids (glycine, sodium glutamate, etc.) | |
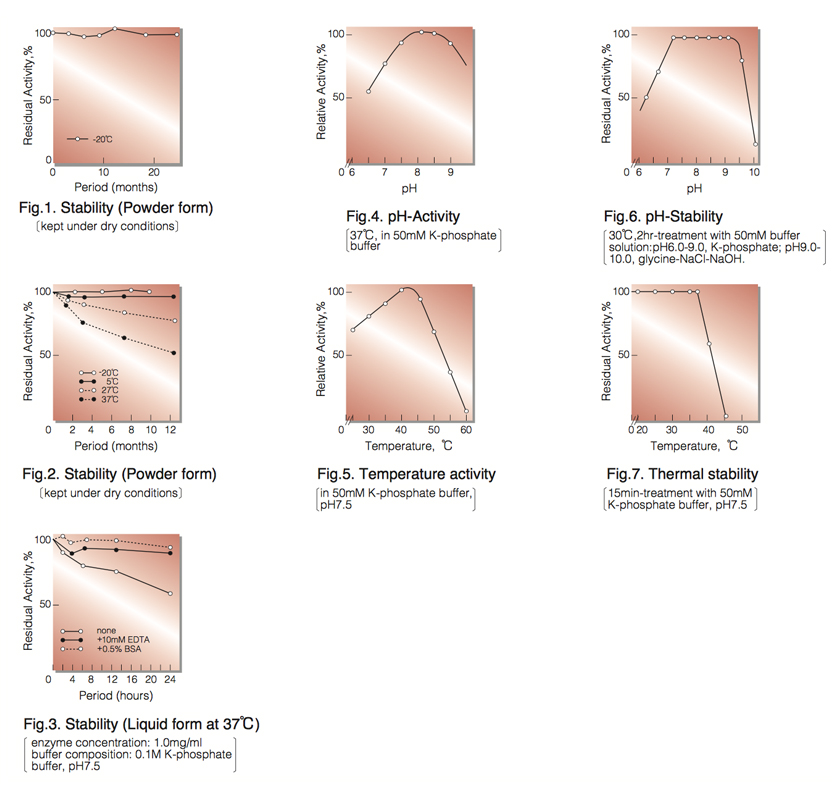
| Stability: | Stable at -20°C for at least One year (Fig.1) |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight: | approx. 95,000 |
| Isoelectric point: | 4.1±0.1 |
| Michaelis constants: | 2.84×10⁻³M (Choline), 5.33×10⁻³M(Betaine aldehyde) |
| Structure: | One mol of FAD is covalently bound to mol of the enzyme⁸⁾ |
| Inhibitors: | p-Chloromercuribenzoate, Cu⁺⁺, Co⁺⁺, Hg⁺⁺, Ag⁺ |
| Optimum pH: | 8.0-8.5(Fig.4) |
| Optimum temperature: | 40-45℃(Fig.5) |
| pH Stability: | pH 7.0-9.0 (30°C, 2 hr)(Fig.6) |
| Thermal stability: | below 37℃ (pH 7.5, 10min)(Fig.7) |
| Effect of various chemicals: | (Table 1) |
APPLICATIONS
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of phospholipids when coupled with phospholipase D and for choline esterase-activity in clinical analysis.⁹~¹¹)
ASSAY
Principle:
choline oxidase
Choline+H₂O+2O₂ ►Betaine+2H₂O₂
peroxidase
2H₂O₂+4-Aminoantipyrine+Phenol ►Quioneimine dye+4H₂O
The appearance of quinoneimine dye is measured at 500nm by spectrophotometry.
Unit definition:
One unit causes the formation of one micromole of hydrogen peroxide (half a micromole of quinoneimine dye) per
minute under the conditions described below.
Method:
| A. Choline chloride solution: | 2.1%[2.1g choline chloride/100ml of Tris-HCl buffer (D)](Should be prepared fresh) |
|---|---|
| B. 4-AA solution: | 1.0% (1.0g 4-aminoantipyrine/100ml of H₂O)(Store at 4℃ in a brownish bottle) |
| C. Phenol solution: | 1.0% (1.0g phenol/100ml of H₂O)(Store at 4℃ in a brownish bottle) |
| D. Tris-HCl buffer: | 0.1M Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.0[Dissolve 12.1g of Tris (MW=121.14) in ca.800ml of H₂O and, after adjusting the pH to 8.0 at 25℃ with 2.0 N HCl, fill up to 1,000ml with H₂O.] |
| E. Enzyme diluent: | 10mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.0 contg. 2mM EDTA and 1.0% KCl. |
Procedure
| Concentration in assay mixture | |
|---|---|
| Tris buffer | 97 mM |
| Choline chloride | 0.14 M |
| EDTA | 33 µM |
| KCI | 2.2 mM |
| 4-Aminoantipyrine | 0.48 mM |
| Phenol | 2.1 mM |
| POD | ca.4.92U/ml |
1. Prepare the following working solution (100ml) in a brownish bottle and store on ice.
97 ml Substrate solution (A)
1.0ml 4-AA solution (B)
2.0ml Phenol solution (C)
5.0mg Peroxidase from horseradish (110 purpurogallin units/mg)(Toyobo GradeIII)
2. Pipette 3.0ml of working solution into a cuvette (d=1.0cm) and equilibrate at 37℃ for about 5 minutes.
3.Add 0.05ml of the enzyme solution* and mix by gentle inversion.
4. Record the increase in optical density at 500nm against the working solution for 3 to 4 minutes in a
spectrophotometer thermostated at 37℃, and calculate theΔOD per minute from the initial linear portion of the curve.
* Dissolve the enzyme preparation in ice-cold Tris-HCl buffer (D) and dilute to 0.1-0.5U/ml with enzyme diluent (E).
Calculation
Activity can be calculated by using the following formula :

ΔOD/min×Vt×df
Volume activity (U/ml) = =ΔOD/min×10.17×df
12.0×1/2×1.0×Vs
Weight activity (U/mg) = (U/ml) × 1/C
- Vt
- : Total volume (3.05ml)
- Vs
- : Sample volume (0.05ml)
- 12.0
- : Millimolar extinction coefficient of quinoneimine dye under the assay conditions(㎠/micromole)
- 1/2
- : Factor based on the fact that one mole of H₂O₂ produces half a mole of quinoneimine dye
- 1.0
- : Light path length (cm)
- df
- : Dilution factor
- C
- : Enzyme concentration in dissolution (c mg/ml)
REFERENCES
- P.J.G Mann and J.H.Quastel; Biochem.J.,31, 869 (1937).
- P.J.G Mann et al; Biochem.J.,32, 1024 (1938).
- H.S.Shieh; Can.J.Microbiol., 10, 837 (1964).
- H.S.Shieh; Ibid.,11, 375 (1965).
- G.J.J.Kortstee; Arch.Mikirobiol., 71, 235 (1970).
- S.Ikuta, K.Matuura, S.Imamura, H.Misaki, Y.Horiuti; J.Biochem., 82, 157 (1977).
- S.Ikuta, S.Imamura, H.Misaki and Y.Horiuti ; J.Biochem., 82, 1741 (1977).
- M.Ohta-Fukuyama, Y.Miyake, S.Emi and T.Yamano; J.Biochem., 88, 197 (1980).
- M.Takayama et al; Clin. Chim. Acta, 79, 93 (1977).
- K.Sugawara and A.Kihara; Eisei Kensa, 27(1), 106 (1978).
- H.Okabe et al ; Clin.Chim.Acta, 80, 87 (1977).
| Chemical | Concn.(mM) | Residual activity(%) |
Chemical | Concn.(mM) | Residual activity(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | − | 100 | MIA | 2.0 | 87 |
| Metal salt | 2.0 | NEM | 2.0 | 100 | |
| MgCl₂ | 87 | IAA | 2.0 | 95 | |
| CaCl₂ | 92 | Hydroxylamine | 2.0 | 77 | |
| Ba(OAc)₂ | 89 | EDTA | 5.0 | 92 | |
| FeCl₃ | 87 | o-Phenanthroline | 2.0 | 90 | |
| CoCl₂ | 89 | α,α′-Dipyridyl | 1.0 | 91 | |
| MnCl₂ | 91 | Borate |
50 | 94 | |
| ZnCl₂ | 88 | NaF | 2.0 | 92 | |
| CdCl₂ | 92 | NaN₃ | 2.0 | 92 | |
| NiCl₂ | 91 | Triton X-100 | 0.10% | 96 | |
| CuSO₄ | 92 | Brij 35 | 0.10% | 92 | |
| Pb(OAc)₂ | 87 | Tween 20 | 0.10% | 95 | |
| AgNO₃ | 80 | Span 20 | 0.10% | 94 | |
| HgCl₂ | 48 | Na-cholate | 0.10% | 96 | |
| 2-Mercaptoethanol | 2.0 | 90 | SDS | 0.05% | 95 |
| PCMB | 1.0 | 13 | DAC | 0.05% | 91 |
Ac, CH₃CO; PCMB, p-Chloromercuribenzoate; MIA, Monoiodoacetate; NEM, N-Ethylmaleimide; IAA, Iodoacetamide; EDTA, Ethylenediaminetetraacetate; SDS, Sodium dodecyl sulfate; DAC, Dimethylbenzylalkylammonium-chloride.
To get a quote, contact us at info@toyobousa.com, or INQUIRY.