DIAPHORASE from Clostridium sp.
DAD-301
NAD(P)H:(acceptor)oxidoreductase(EC 1.6.99.-)
NAD(P)H+ H⁺+ Acceptor(ox) ► NAD(P) ⁺+ Acceptor(red)
| Appearance: | Yellowish amorphous powder, lyophilized | |
|---|---|---|
| Activity: | GradeⅢ 30U/mg-solid or more (containing approx. 15% of stabilizers) |
|
| Contaminants: | Myokinase ≤5.0×10⁻¹% NAD(P)H oxidase ≤5.0×10⁻¹% |
|
| Stabilizers: | FMN, NAD(P)H | |
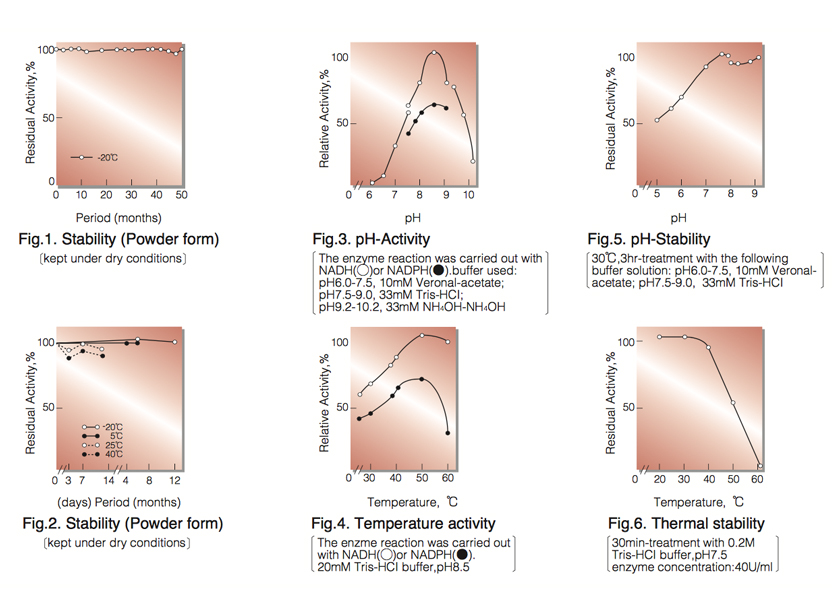
| Stability: | Stable at -20°C for at least Two years (Fig.1) |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight: | 24,000 ¹ ⁾ |
| Michaelis constants: | 2.0×10⁻⁵M (NADH), 6.0×10⁻⁶M (NADPH) |
| Structure: | One mol of FMN per mol of enzyme ¹ ⁾ |
| Inhibitor: | N-Ethylmaleimide |
| Optimum pH: | 8.5(Fig.3) |
| Optimum temperature:: | 50℃(Fig.4) |
| pH Stability: | pH 7.5 (30℃, 3hr)(Fig.5) |
| Thermal stability: | below 30℃ (pH 7.5, 30min)(Fig.6) |
| Substrate specificty: | Either NADH or NADPH can be used as a reductant. The catalytic ratio (NADPH/NADH) is 0.6 in the assay method. Neither oxygen nor cytochrome C can be utilized as a hydrogen acceptor. |
APPLICATIONS
This enzyme is useful for colorimetric determination of NAD(P)H and many dehydrogenases when coupled with various dyes which act as hydrogen acceptors from NAD(P)H.
ASSAY
Principle:
diaphorase
NADH+H⁺+DCPIP ►NAD⁺+Leucodye
The reduction of DCPIP (2,6-dichlorophenol-indophenol) is measured at 600nm by spectrophotometry.
Unit definition:
One unit causes the decrease of one unit absorbance (1.0) of DCPIP per minute under the condeitions described
below.
Method:
| A. Buffer solution: | 0.2M Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 |
|---|---|
| B. NADH solution: | 6.0mM (Prepare freshly and store on ice) |
| C. DCPIP solution: | 1.2mM [3.9mg DCPIP・2H₂O/10ml of H₂O](Should be prepared fresh) |
| D. Enzyme diluent: | Buffer solution(A) containing 0.1% of bovine serum albumin. |
Procedure
| Concentration in assay mixture | |
|---|---|
| Tris buffer | 27 mM |
| NADH | 0.20mM |
| DCPIP | 40 µM |
| BSA | ca.33µg/ml |
1. Prepare the following reaction mixture in a cuvette (d=1.0cm) and equilibrate at 25℃ for about 5 minutes.
2.4 ml H₂O
0.3ml Buffer solution (A)
0.1ml NADH solution (B)
2. Add 0.1ml each of the enzyme solution* and DCPIP solution (C) in this order and mix by rapid inversion.
3. Record the decrease of optical density at 600nm against water for 2 to 3 minutes in a spectrophotometer thermostated at 25°C, and calculate theΔOD per minute from the initial linear portion of the curve (ΔOD test).
At the same time, measure the blank rate (ΔOD blank) by using the same method as the test except that
the enzyme diluent is added instead of the enzyme solution.
* Dissolve the enzyme preparation in ice-cold buffer solution (A) (approx.1.0% solution), dilute to 0.4− 0.8U/ml with ice-cold enzyme diluent (D) and store on ice.
Calculation
Activity can be calculated by using the following formula :

ΔOD/min (ΔOD test−ΔOD blank ) × df
Volume activity (U/ml) = =ΔOD/min×10×df
1.0×Vs
Weight activity (U/mg) = (U/ml) × 1/C
- Vs
- : Sample volume (0.1ml)
- 1.0
- : Unit absorbance at 600nm due to unit definition
- df
- : Dilution factor
- C
- : Enzyme concentration in dissolution (c mg/ml)
REFERENCES
- F.Kaplan, P.Setlow and N.O.Kaplan; Arch,Biochem.Biophys., 132, 91 (1969).
| Chemical | Concn.(mM) | Residual activity(%) |
Chemical | Concn.(mM) | Residual activity(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | − | 100 | NaF | 2.0 | 102 |
| Metal salt | 2.0 | NaN₃ | 2.0 | 100 | |
| MgCl₂ |
99 | EDTA | 5.0 | 99 | |
| CaCl₂ | 102 | o-Phenanthroline | 2.0 | 99 | |
| Ba(OAc)₂ | 100 | α,α′-Dipyridyl | 1.0 | 101 | |
| FeCl₂ | 90 | Borate |
5.0 | 100 | |
| CoCl₂ | 101 | IAA | 2.0 | 99 | |
| MnCl₂ | 96 | NEM | 2.0 | 100 | |
| ZnCl₂ | 100 | Hydroxylamine | 2.0 | 101 | |
| Cd(OAc)₂ | 100 | TritonX-100 | 0.10% | 106 | |
| NiCl₂ | 99 | Brij 35 | 0.10% | 104 | |
| CuSO₄ | 87 | Tween 20 |
0.10% | 107 | |
| Pb(OAc)₂ | 88 | Span 20 | 0.10% | 101 | |
| AgNO₃ | 103 | Na-Cholate | 0.10% | 99 | |
| HgCl₂ | 103 | SDS | 0.05% | 32 | |
| PCMB | 2.0 | 90 | DAC | 0.05% | 32 |
| MIA | 1.0 | 100 |
To get a quote, contact us at info@toyobousa.com, or INQUIRY.