ß-GALACTOSIDASE from Escherichia coli
GAH-201
| Appearance: | White amorphous powder, lyophilized. | |
|---|---|---|
| Activity: | GradeⅡ 500U/mg-solid or more | |
| Contaminants: | α-galactosidase <1×10⁻⁴% α-glucosidase <1×10⁻⁴% ß-glucosidase <2×10⁻³% α-mannosidase <1×10⁻⁴% ß-mannosidase <1×10⁻⁴% proteinase <10mAbs/mg-P |
|
| Stabilizer: | Mg⁺⁺ | |
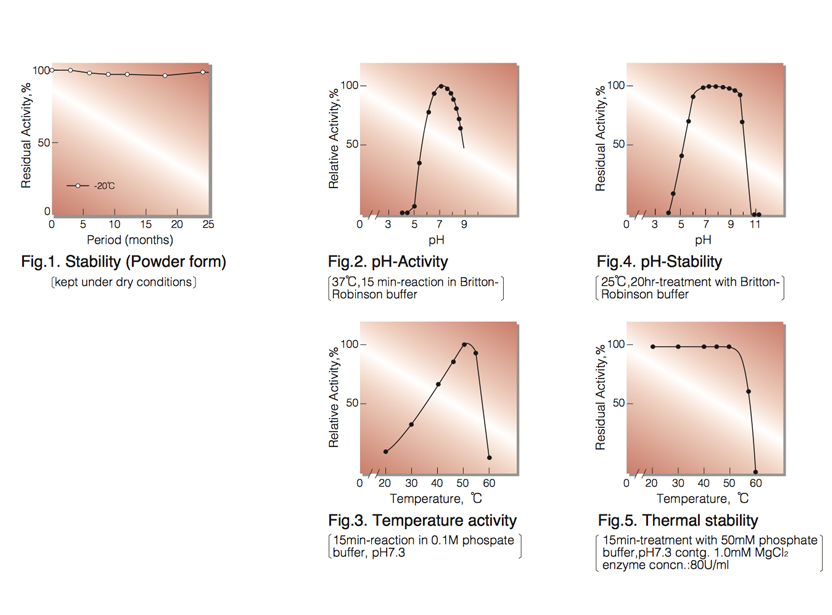
| Stability: | Stable at -20°C for at least One year (Fig.1) |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight: | 540,000 ¹· ² ⁾ |
| Isoelectric point ³⁾: | 4.6 |
| Michaelis constants: | 3.0×10⁻⁴M (o-Nitrophenyl-ß-D-galactoside), 6.7×10⁻⁵M (p- Nitrophenyl-ß-D-galactoside), 2.3×10⁻⁴M (Phenyl-ß-D-galactoside), 2.5×10⁻³M (Lactose) |
| Structure ⁴ ˜ ⁸⁾: | The enzyme is composed of four identical subunits having a molecular weight of ca.135,000. The amino acid analysis indicates approximately 1,170 residues per subunit. |
| Inhibitors: | p-Chloromercuribenzoate, lodoacetamide, heavy metal ions (Zn⁺⁺, Fe⁺⁺⁺, Cd⁺⁺, Cu⁺⁺, Pb⁺⁺, Ag⁺, Hg⁺⁺), lonic detergents (SDS, DAC, etc.) |
| Optimum pH: | 7.0-7.5(Fig.2) |
| Optimum temperature:: | 50-55℃(Fig.3) |
| pH Stability: | pH 6.5-8.5 (25℃, 20hr)(Fig.4) |
| Thermal stability: | below 50℃ (pH 7.3, 15min)(Fig.5) |
| Substrate specificty: | The enzyme specifically hydrolyzes ß-D-galactosyl linkage (Table 1). |
| Effect of various chemicals: | (Table 2) |
APPLICATIONS
This enzyme is useful for structural investigation of carbohydrates, the determination of lactose (foodstuff analysis) and as an enzyme label for enzyme immunoassay.
ASSAY
Principle:
ß-galactosidase
o-Nitrophenyl-ß-D-galactopyranoside (ONPG) ►o-Nitrophenol (ONP)+D-Galactose
The appearance of o-nitrophenol is measured at 410nm by spectrophotometry.
Unit definition:
One unit causes the formation of one micromole of ONP per minute under the conditions described below.
Method:
| A. Phosphate buffer, pH 7.3: | 0.1M (Prepare by mixing 0.1M Na₂HPO₄ and 0.1M KH₂PO₄ to reach pH 7.3 at 37℃.) |
|---|---|
| B. Mercaptoethanol solution: | 3.36M [Dilute 4.0ml of 2-mercaptoethanol (14.2M) to 17ml with H₂O.] (Should be prepared fresh) |
| C. MgCl₂ solution: | 30mM (Dissolve 610mg of MgCl₂・6H₂O in about 80ml of H₂O and, after adjusting the pH to 7.3 with 1.0 N NaOH, fill up to 100ml with H₂O.) |
| D. ONPG solution: | 34mM (205mg ONPG/20ml of Reagent A)(Stable for one week if stored at 0-5℃) |
| E. Enzyme diluent: | 50mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.3 contg. 1.0mM MgCl₂ and 0.1% BSA |
Procedure
| Concentration in assay mixture | |
|---|---|
| Phosphate buffer | 92 mM |
| ONPG | 2.3mM |
| Mercaptoethanol | 0.11 M |
| MgCl₂ | 1.0mM |
1. Prepare the following reaction mixture in a cuvette (d=1.0cm) and equilibrate at 37°C for about 5 minutes.
2.5 ml 0.1M Phosphate buffer,pH 7.3 (A)
0.1ml Mercaptoethanol solution (B)
0.1ml MgCl₂ solution(C)
0.2ml ONPG solution (D)
2. Add 0.1ml of the enzyme solution* and mix by gentle inversion.
3. Record the increase in optical density at 410nm against water for 2 to 3 minutes in a spectrophotometer
thermostated at 37°C, and calculate ΔOD per minute from the initial linear portion of the curve (ΔOD test).
At the same time, measure the blank rate (ΔOD blank) by using the same method as the test except that the enzyme diluent (E) is added instead of the enzyme solution.
* Dilute the enzyme preparation to 0.17-0.85U/ml with ice-cold enzyme diluent (E).
Calculation
Activity can be calculated by using the following formula :

ΔOD/min (ΔOD test−ΔOD blank ) ×Vt × df
Volume activity (U/ml) = =ΔOD/min×8.57×df
3.5×1.0×Vs
- Vt
- : Total volume (3.0ml)
- Vs
- : Sample volume (0.1ml)
- 3.5
- : Millimolar extinction coefficient of ONP under the assay condition (㎠/micromole)
- 1.0
- : Light path length (cm)
- df
- : Dilution factor
REFERENCES
- G.R.Graben, E.Steers, Jr.and C.B.Anfinsen; J.Biol.Chem., 240, 2468 (1965).
- C.C.Contaxis and F.J.Reithel; Biochem,J., 124, 623 (1971).
- K.Wallenfels and R.Weil; The Enzymes,Vol. 7, p.617 (P.D.Boyer ed.), Academic Press. New York-London
(1972). - A.Ulmann, M.E.Goldberg, D.Perrin and J.Monod; Biochemistry, 7, 261 (1968).
- A.V.Fowler and I.Zabin; J.Biol.Chem., 245, 5032 (1970).
- A.V.Fowler and I.Zabin; J.Biol.Chem., 247, 5425, 5432 (1972).
- F.Melchers and W.Messer; Eur.J.Biochem., 34, 228 (1973).
- K.E.Langley, A.V.Fowler and I.Zabin; J.Biol.Chem., 250, 2587 (1975).
| Substrate (2.3mM) | Relative activity (%) |
Vmax** (Relative value) |
Substrate (2.3mM) | Relative activity (%) |
Vmax** (Relative value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| o-Nitrophenyl-ß-D-galactopyranoside | 100 | 100 | p-Nitrophenyl-α-D-mannopyranoside | 0 | 0 |
| p-Nitrophenyl-ß-D-galactopyranoside | 14.7 | 13.4 | p-Nitrophenyl-ß-D-mannopyranoside | 0 | 0 |
| Phenyl-ß-D-galactopyranoside* | 1.1 | 1.3 | p-Nitrophenyl-α-L-fucopyranoside | 0 | 0 |
| Lactose* | 2.1 | 3.9 | p-Nitrophenyl-ß-L-fucopyranoside | 0 | 0 |
| p-Nitrophenyl-α-D-galactopyranoside | 0 | 0 | p-Nitrophenyl-α-D-xylopyranoside | 0 | 0 |
| p-Nitrophenyl-α-D-glucopyranoside | 0 | 0 | p-Nitrophenyl-ß-D-xylopyranoside | 0 | 0 |
| p-Nitrophenyl-ß-D-glucopyranoside | 0 | 0 |
| Chemical | Concn.(mM) | Residual activity(%) |
Chemical | Concn.(mM) | Residual activity(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | − | 100 | MIA | 2.0 | 86 |
| Metal salt | 2.0 | NEM | 2.0 | 95 | |
| MgCl₂ |
99 | IAA | 2.0 | 1.4 | |
| CaCl₂ | 102 | Hydroxylamine | 2.0 | 78 | |
| Ba(OAc)₂ | 80 | EDTA | 5.0 | 103 | |
| FeCl₃ | 59 | o-Phenanthroline |
2.0 | 99 | |
| CoCl₂ | 83 | α,α′-Dipyridy | 2.0 | 103 | |
| MnCl₂ | 100 | Borate | 50 | 98 | |
| ZnSO₄ | 6.2 | NaF | 2.0 | 99 | |
| Cd(OAc)₂ | 4.7 | NaN₃ | 20 | 98 | |
| NiCl₂ | 77 | Triton X-100 | 0.1% | 101 | |
| CuSO₄ | 0.9 | Brij 35 | 0.1% | 103 | |
| Pb(OAc)₂ | 1.3 | Tween 20 |
0.1% | 103 | |
| AgNO₃ | 0 | Span 20 | 0.1% | 107 | |
| HgCl₂ | 2.0 | Na-cholate | 0.1% | 109 | |
| Mercaptoethanol | 2.0 | 99 | SDS | 0.05% | 75 |
| Cysteine | 2.0 | 102 | DAC | 0.05% | 0 |
| PCMB | 2.0 | 0.3 |
Ac, CH₃CO; PCMB, p-Chloromercuribenzoate; MIA, Monoiodoacetate; NEM, N-Ethylmaleimide; IAA, lodoacetamide; EDTA, Ethylenediaminetetraacetate; SDS, Sodium dodecyl sulfate; DAC, Dimethylbenzylalkylammonium chloride.