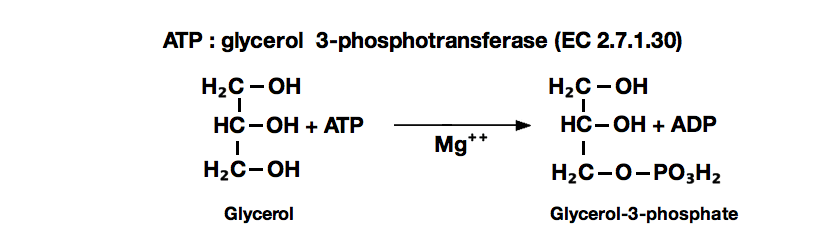
GLYCEROL KINASE from Cellulomonas sp.
GYK-301
| Appearance: | White amorphous powder, lyophilized | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Activity: | GradeⅢ 20 U/mg-solid or more (containing approx. 50% of stabilizers) |
||
| Contaminants: | NADH oxidase ≤1.0×10⁻²% Catalase ≤1.0×10⁻¹% Phosphatase (pH 6.0) ≤2.0×10⁻³% |
||
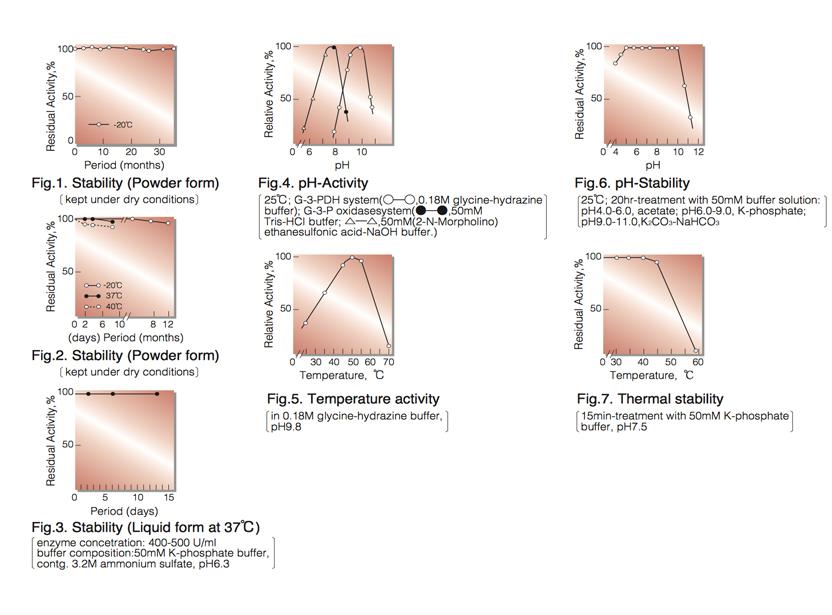
| Stability: | Stable at -20°C for at least One year (Fig.1) |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight : | approx. 128,000 (by gel filtration) |
| Isoelectric point: | 4.2 |
| Michaelis constants : | 4.4×10⁻⁵M (Glycerol), 4.3×10⁻⁴M (ATP) |
| Inhibitors: | p-Chloromercuribenzoate, heavy metal ions (Pb⁺⁺, Fe⁺⁺, Hg⁺⁺, Ag⁺) |
| Optimum pH : | 9.8 (G-3-PDH system), 7.8 (G-3-P oxidase system)(Fig.4) |
| Optimum temperature: | 50°C(Fig.5) |
| pH Stability: | pH 5.5-10.0 (25°C, 20hr)(Fig.6) |
| Thermal stability: | below 40°C (pH 7.5, 15min)(Fig.7) |
| Substrate specificity: | This enzyme catalyzes the stereospecific transfer of the terminal phosphoryl moiety of ATP to one of the primary hydroxyl group of glycerol, forming sn-glycerol-3-P. The enzyme has the highest specificity for glycerol, and also phosphorylates dihydroxyacetone and glyceraldehyde (Table 1,2). Mg⁺⁺ is essentially required for the reaction. |
| Effect of various chemicals: | (Table 3) |
APPLICATIONS
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of glycerol and triglyceride when coupled with glycerol-3-phosphate oxidase (=G-3-P oxidase, G3O-321) or pyruvate kinase and lactate dehydrogenase (LCD-209, LCD-211, LCD-221), lipoprotein lipase (LPL-311, LPL-314) in clinical analysis.
ASSAY
Principle ¹ ⁾:
glycerol kinase
Glycerol+ATP ► Glycerol-3-P+ADP
Mg⁺⁺
G-3-PDH
Glycerol-3-P+NAD⁺ ► Dihydroxyacetone-P+NADH+H⁺
The appearance of NADH is measured at 340nm by spectrophotometry.
Unit definition:
One unit causes the formation of one micromole of NADH per minute under the conditions described below.
Method:
| A. Glycine-hydrazine buffer,: pH 9.8 |
0.2M[Weigh 1.5g of glycine and 20.8g of hydrazine hydrate (MW= 50.06), dissolve in 70ml of H₂O, add 0.4ml of 1.0M MgCl₂ and after adjusting the pH to 9.8 with 2.0N HCl or 2.0N KOH, fill up to 100ml with H₂O] |
|---|---|
| B. Glycerol solution: | 0.1M (Should be prepared fresh) |
| C. ATP solution: | 0.1M (Should be prepared fresh) |
| D. NAD⁺ solution: | 14mM (Should be prepared fresh) |
| E. Glycerol-3-phosphate: dehydrogenase (G-3-PDH) solution | Crystalline suspension in 3.2M ammonium sulfate solution (10mg/ml, ca. 60 U/mg from Roche) |
| F. Enzyme diluent: | 20mM K-phosphate buffer pH 7.5 containing 0.2% BSA |
Procedure
| Concentration in assay mixture | |
|---|---|
| Glycine buffer | 0.18 M |
| Glycerol | 3.0 mM |
| ATP | 1.5 mM |
| NAD⁺ |
0.42mM |
| MgCl₂ | 3.6 mM |
| G-3-P DH | ca.5.4 U/ml |
1. Prepare the following reaction mixture in a cuvette (d=1.0cm) and equilibrate at 25°C for about 5 minutes.
3.0 ml 0.2M Glycine-hydrazine buffer, pH 9.8 (A)
0.10 ml Substrate solution (B)
0.05 ml ATP solution (C)
0.10 ml NAD⁺ solution (D)
0.03 ml G-3-PDH solution (E)
2. Add 0.05ml of the enzyme solution* and mix by gentle inversion.
3. Record the increase in optical density at 340nm against water for 3 to 4 minutes in a spectrophotometer
thermostated at 25°C and calculate theΔOD per minute from the initial linear portion of the curve (ΔOD test).
At the same time, measure the blank rate (ΔOD blank) by using the same method as the test except that the enzyme diluent is added instead of the enzyme solution.
* Dissolve the enzyme preparation in ice-cold enzyme diluent (F), dilute to 0.2-0.4U/ml with the same buffer and store on ice.
Calculation
Activity can be calculated by using the following formula :

ΔOD/min (ΔOD test−ΔOD blank ) ×Vt × df
Volume activity (U/ml) = =ΔOD/min×10.7×df
6.22×1.0×Vs
Weight activity (U/mg)=(U/ml)×1/C
- Vt
- : Total volume (3.33ml)
- Vs
- : Sample volume (0.05ml)
- 6.22
- : Millimolar extinction coefficient of NADH (㎠/micromole)
- 1.0
- : Light path length (cm)
- df
- : Dilution factor
- C
- : Enzyme concentration in dissolution (c mg/ml)
REFERENCES
- Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, vol. 1, p.468 (H.U.Bergmeyer ed., 2nd English Edition), Verlag Chemie Weinheim & Academic Press, New York-London (1974).
- S.Hayashi and E.C.C.Lin.; J.Biol.Chem., 212, 1030 (1967).
| Substrate (6mM) | Relative activity(%) | Substrate (6mM) | Relative activity(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerol | 100 | 2,3-Butanediol | ― |
| Glycerol-α-monochlorohydrin | 0.09 |
D-Mannitol | ― |
| Ethylene glycol | ― |
D-Sorbitol |
― |
| 1,2-Propanediol | ― | D-Glucose | ― |
| 1,3-Propanediol | 0.07 | Ribitol | ― |
| 1,3-Butanediol | ― | Methanol | ― |
| 1,4-Butanediol | ― | Ethanol | ― |
―, Not detected
| Substrate | Km (M) | Vmax(Relative value) |
|---|---|---|
| Glycerol | 4.4×10⁻⁵* | 100 |
| Dihydroxyacetone | 6.0×10⁻³ |
152 |
| D,L-Glyceraldehyde | 5.8×10⁻³ |
76 |
*This value was taken from that determined by G-3-PDH system, pH 9.8.
| Chemical | Concn.(mM) | Residual activity(%) |
Chemical | Concn.(mM) | Residual activity(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | − | 100 | PCMB | 2.0 | 22 |
| Metal salt | 2.0 | MIA | 2.0 | 96 | |
| MgCl₂ | 100 |
NaF | 2.0 | 97 | |
| CaCl₂ |
100 | NaN₃ | 20 | 97 |
|
| Ba(OAc)₂ | 100 |
EDTA | 5.0 | 101 | |
| FeCl₃ | 75 |
o-Phenanthroline | 2.0 | 96 | |
| CoCl₂ | 100 | α,α′-Dipyridyl | 2.0 | 92 | |
| MnCl₂ | 100 | Borate | 50 | 100 | |
| Zn(OAc)₂ | 99 |
Triton X-100 | 0.1% | 99 | |
| NiCl₂ | 98 |
Na-cholate | 0.1% | 97 | |
| CuSO₄ | 100 | ||||
| Pb(OAc)₂ | 88 | ||||
| AgNO₃ | 0 | ||||
| HgCl₂ | 0 |
Ac, CH₃CO; PCMB, p-Chloromercuribenzoate; MIA, Monoiodoacetate.
To get a quote, contact us at info@toyobousa.com, or INQUIRY.