PEROXIDASE from Horseradish
PEO-131, 301, 302
Donor:hydrogen-peroxidase oxidoreductase (EC 1.11.1.7)
Donor + H₂O₂ ► Oxidized donor + 2H₂O
Donor:hydrogen-peroxidase oxidoreductase (EC 1.11.1.7)
Donor + H₂O₂ ► Oxidized donor + 2H₂O
| Appearance: | Reddish-brown amorphous powder, lyophilized |
|---|---|
| Activity: | GradeⅠ 250 Purpurogallin U/mg-solid or more (-131) (RZ ≥ 3.0, salt free) GradeⅢ 110 Purpurogallin U/mg-solid or more (-301) (RZ ≥ 2.0, containing approx. 30% of stabilizers) GradeⅢ 180 Purpurogallin U/mg-solid or more (-302) (RZ ≥ 2.0, salt free) |
| Contaminant: | Phosphatase ≤1.0×10⁻³% (GradeⅢ) |
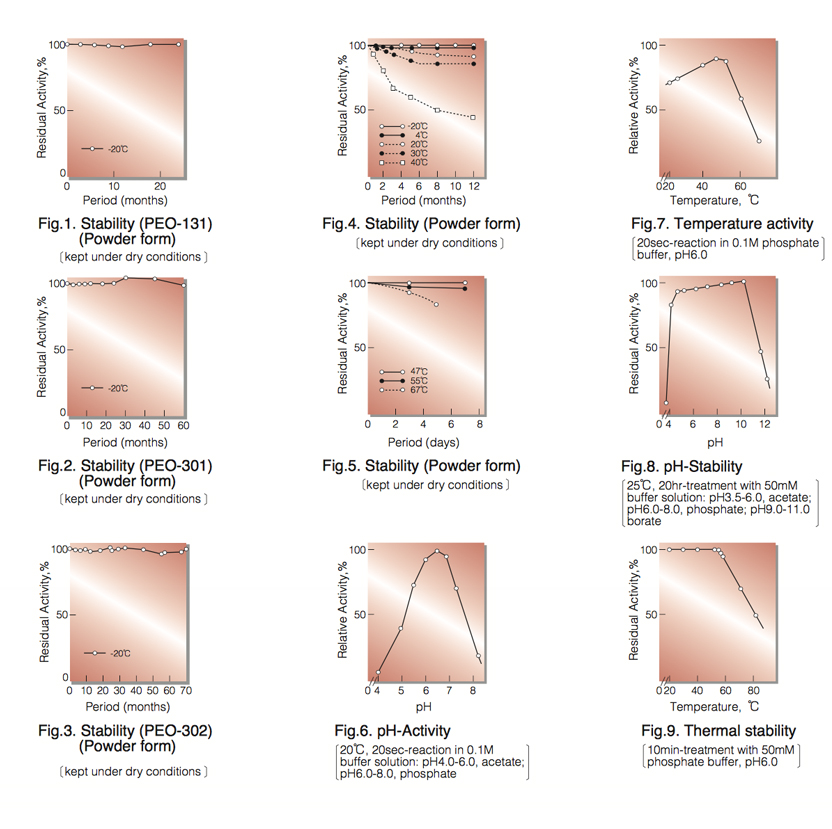
| Stability: | Stable at -20°C for at least Two years (Fig.1,2,3) |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight : | approx. 40,000 |
| Structure: | Glycoprotein with one mole of protohaemin IX ² ⁾ |
| Inhibitors: | Cyanide, sulfide, fluoride, azide ³ ⁾ |
| Optimum pH : | 6.0-7.0(Fig.6) |
| Optimum temperature : | 45°C(Fig.7) |
| pH Stability : | pH 5.0-10.0 (25°C, 20hr)(Fig.8) |
| Thermal stability : | below 50°C (pH 6.0, 10min)(Fig.9) |
| Effect of various chemicals : | (Table 1) |
APPLICATIONS ⁴ ˜¹¹⁾
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of H₂O₂ in clinical analysis. Especially, the highly purified preparation (Grade I) is useful as a protein tracer in histo-and cyto-chemistry and as a valuable experimental tool in hodological neurography. Also, the enzyme preparation has been used as an enzyme label in enzyme immunoassay. Grade III(-302) is suitable for dry chemistry. On the other hand, the enzymes contribute for the reduction of phehol in waste water.
ASSAY
Principle:
peroxidase
2Pyrogallol+3H₂O₂ ► Purpurogallin+5H₂O+CO₂
The appearance of Purpurogallin is measured at 420nm by spectrophotometry.
Unit definition:
One purpurogallin unit causes the formation of one milligram of purpurogallin in 20 seconds under the conditions
described below.
Method:
| A. Pyrogallol solution: | 5% (W/V)(Should be prepared fresh). |
|---|---|
| B. H₂O₂ solution: | 0.147M[Dilute 1.67ml of 30% (W/V) H₂O₂ to 100ml with H₂O](Should be prepared fresh) |
| C. Phosphate buffer, pH6.0: | 0.1M |
| D. H₂SO₄ solution: | 2.0N |
Procedure
| Concentration in assay mixture | |
|---|---|
| Phosphate buffer | 15 mM |
| Pyrogallol | 40 mM |
| H₂O₂ | 7.4mM |
1. Prepare the following reaction mixture in a test tube (32ϕ ×200mm) and equilibrate at 20°C for about 5 minutes.
14.0ml H₂O
2.0ml Pyrogallol solution (A)
1.0ml H₂O₂ solution (B)
2.0ml Phosphate buffer, pH6.0 (C)
2. Add 1.0ml of the enzyme solution* and mix.
3. After exactly 20 seconds at 20°C, add 1.0ml of 2.0 N H₂SO₄ solution (D) to stop the reaction.
4. Extract the produced purpurogallin from the above stopped reaction mixture in five times with 15ml portions
of ether and fill up the combined ether extracts to 100ml with fresh ether.
5. Measure the optical density at 420nm against water (OD test).
At the same time, prepare the blank by first mixing the reaction mixture with 1.0ml of 2.0 N H₂SO₄ solution (D) after 20 a sec-incubation at 20°C, followed by the addition of the enzyme solution and extracting with ether by the same procedure as the test (OD blank).
* Dissolve the enzyme preparation in ice-cold 0.1M phosphate buffer, pH 6.0 (C), dilute to 3.0-6.0 pur purogallin U/ml with the same buffer and store on ice.
Calculation
Activity** can be calculated by using the following formula :

ΔOD (OD test- OD blank)×df
Volume activity (U/ml) = = ΔOD×8.547×df
0.117×Vs
Weight activity (U/mg)=(U/ml)×1/C
- Vs
- : Sample volume (1.0ml)
- 0.117
- : Optical density at 420 nm corresponding to 1mg% of Purpurogallin in ether.
- df
- : Dilution factor
- C
- : Enzyme concentration in dissolution (c mg/ml)
- **One purpurogallin unit is equivalent to 13.5 international units determined with o-dianisidine at 25°C.
REFERENCES
- K.G.Paul and T.Stigbrand; Acta Chem.Scand., 24, 3607 (1970).
- L.M.Shannon et al.; J.Biol.Chem., 241, 2166 (1966).
- E.Kay et al.; J.Biol.Chem., 242, 2470 (1967).
- R.Lasek et al.; Brain Res., 8, 319 (1968).
- W.M.Cowan et al.; Brain Res , 37, 21 (1972).
- J.H.La Vail et al.; Brain Res., 58, 470 (1973).
- A.M.Graybiel and M.Devor; Brain Res., 68, 167 (1974).
- A.H.Bunt et al.; Brain Res., 102, 152 (1976).
- D.R.Colman et al.; Brain Res., 102, 156 (1976).
- M.Dubois-Dalcq et al.; J.Histochem.Cytochem., 25, 1201 (1977).
- M.Sato et al.; Brain Res., 140, 149 (1978).
| Chemical | Concn.(mM) | Residual activity(%) |
Chemical | Concn.(mM) | Residual activity(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | − | 100 | MIA | 2.0 | 99 |
| Metal salt | 2.0 | NEM | 2.0 | 97 | |
| MgCl₂ | 102 | IAA | 2.0 | 99 | |
| CaCl₂ | 102 | Hydroxylamine | 2.0 | 98 | |
| Ba(OAc)₂ | 105 | EDTA | 5.0 | 95 |
|
| FeCl₃ | 98 | o-Phenanthroline | 2.0 | 98 | |
| CoCl₂ | 97 | α,α′-Dipyridyl | 1.0 | 96 |
|
| MnCl₂ | 97 |
Borate | 50 | 98 | |
| ZnCl₂ | 99 |
NaF | 2.0 | 98 | |
| CdCl₂ | 99 | NaN₃ |
2.0 | 75 | |
| NiCl₂ | 96 | Triton X-100 | 0.10% | 98 |
|
| CuSO₄ | 98 | Brij 35 | 0.10% | 80 | |
| Pb(OAc)₂ | 96 | Tween 20 | 0.10% | 89 | |
| AgNO₃ | 91 | Span 20 | 0.10% | 98 | |
| HgCl₂ | 92 | Na-cholate | 0.10% | 97 | |
| 2-Mercaptoethanol |
2.0 | 94 | SDS |
0.05% | 98 |
| PCMB | 1.0 | 98 | DAC | 0.05% | 102 |
※Residual activity was measured by 4AA-DEA method
4AA, 4-Aminoantipyrine; DEA, Diethylaniline
Ac, CH₃CO; PCMB, p-Chloromercuribenzoate; MIA, Monoiodoacetate; NEM, N-Ethylmaleimide; IAA, Iodoacetamide; EDTA, Ethylenediaminetetraacetate; SDS, Sodium dodecyl sulfate; DAC, Dimethylbenzylalkylammonium chloride.
To get a quote, contact us at info@toyobousa.com, or INQUIRY.