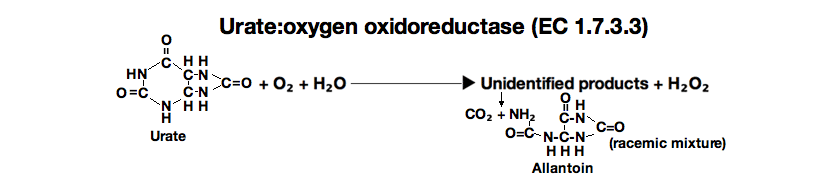
URICASE from Bacillus sp
UAO-211
| Appearance: | White amorphous powder, lyophilized |
|---|---|
| Activity: | GradeⅡ 1.5U/mg-solid or more |
| Contaminant: | Catalase ≤1.0% |
| Stabilizers: | Borate, EDTA, nonionic detergents |
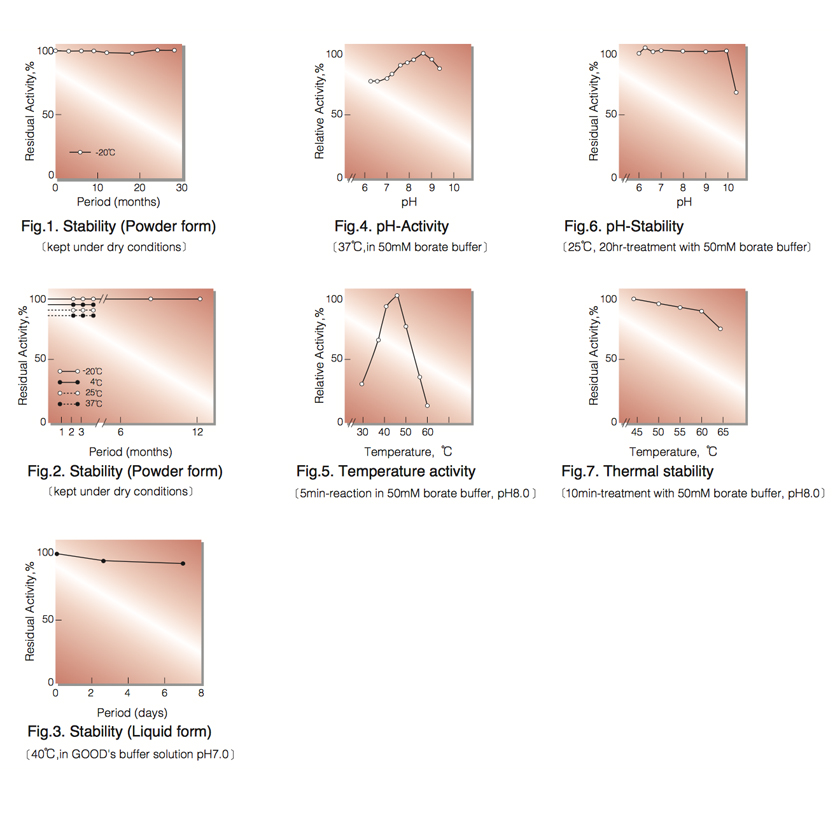
| Stability: | Stable at -20°C for at least One year (Fig.1) |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight : | approx.150,000 |
| Structure: | 4 subunits per molecule |
| Isoelectric point : | 4.7 |
| Michaelis constant: | 1.36×10⁻⁵M (Uric acid) |
| Inhibitors: | Ag⁺,Hg⁺⁺ |
| Optimum pH : | 8.5(Fig.4) |
| Optimum temperature : | 45°C(Fig.5) |
| pH Stability : | pH 6.0-9.5 (25°C, 20hr)(Fig.6) |
| Thermal stability : | below 60°C (pH 8.0, 10min)(Fig.7) |
| Effect of various chemicals: | (Table 1) |
APPLICATIONS
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of uric acid in clinical analysis.
ASSAY
Principle:
uricase
Uric acid+O₂+2H₂O ► Allantoin+H₂O₂+CO₂
The disappearance of uric acid is measured at 290nm by spectrophotometry.
Unit definition:
One unit causes the oxidation of one micromole of uric acid per minute under the conditions described below.
Method:
| A. Uric acid solution: | 0.001%[Dilute the stock solution (0.01%) to 10-fold volume with 50mM borate buffer containing 0.001% Triton X-100 and 1.0mM EDTA, pH 8.0](Should be prepared fresh) Stock solution : 10.0mg uric acid/100ml of above buffer (Store at 0-5°C) |
|---|---|
| B. KOH solution: | 20% |
| C. Enzyme diluent : | 50mM borate buffer containing 0.001% Triton X-100 and 1.0mM EDTA, pH 8.0 |
Procedure
| Concentration in assay mixture | |
|---|---|
| Borate buffer | 42 mM |
| Uric acid | 40 µM |
| EDTA | 0.83 mM |
| Triton X-100 | 0.00083% |
1. Prepare the following reaction mixture in a test tube and equilibrate at 37°C for about 5 minutes.
2.0ml Uric acid solution (A)
0.5ml Distilled water
2. Add 0.5ml of the enzyme solution* and mix by gentle inversion.
3. After exactly 5 minutes at 37°C, add 0.2ml of 20% KOH solution (B) to stop the reaction and measure the
optical density at 290nm against water (OD test).
At the same time, prepare the blank by first mixing the reaction mixture with 0.2ml of KOH solution after
5min-incubation at 37°C, followed by the addition of the enzyme solution (OD blank).
* Dissolve the enzyme preparation in ice-cold enzyme diluent (C) and dilute to 0.01−0.02U/ml with the same buffer and store on ice.
Calculation
Activity can be calculated by using the following formula :

ΔOD (OD blank-OD test)×Vt×df
Volume activity (U/ml) = = ΔOD×0.105×df
12.2 ×1.0× t × Vs
Weight activity (U/mg)=(U/ml)×1/C
- Vt
- : Total volume (3.2ml)
- Vs
- : Sample volume (0.5ml)
- 12.2
- : Millimolar extinction coefficient of uric acid (㎠/micromole)
- t
- : Reaction time (5 minutes)
- 1.0
- : Light path length (cm)
- df
- : Dilution factor
- C
- : Enzyme concentration in dissolution (c mg/ml)
REFERENCES
- S.Asano, K.Yamamoto, S.Teshima, T.Kikuchi and Y.Kawamura; Rinsho Kagaku, 23 (3), 214 (1994)
- K.Yamamoto, Y.Kojima, T.Kikuchi, T.Shigyo, K.Sugihara, M.Takashio and S.Emi; J.Biochem. 119, 80 (1996)
| Chemical | Concn.(mM) | Residual activity(%) |
Chemical | Concn.(mM) | Residual activity(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | − | 100 | EDTA | 5.0 | 104 |
| Metal salt |
2.0 | o-Phenanthroline | 2.0 | 91 | |
| MgCl₂ | 89 |
α,α′-Dipyridyl | 1.0 | 89 | |
| CaCl₂ |
91 | Borate | 50 | 102 | |
| Ba(OAc)₂ | 118 |
IAA | 2.0 | 93 | |
| FeCl₃ | 95 | NEM | 2.0 | 107 | |
| CoCl₂ | 91 | Hydroxylamine | 2.0 | 91 | |
| MnCl₂ | 93 | 2-Mercaptoethanol | 2.0 | 104 | |
| ZnSO₄ | 91 | Triton X-100 | 0.10% | 93 | |
| Cd(OAc)₂ | 87 | Brij 35 | 0.10% | 93 | |
| NiCl₂ | 89 | Tween 20 | 0.10% | 98 | |
| CuSO₂ | 78 | Span 20 | 0.10% | 103 | |
| Pb(OAc)₂ | 91 | Na-cholate | 0.10% | 98 | |
| AgNO₃ | 44 | SDS |
0.05% | 91 | |
| HgCl₂ | 46 | DAC | 0.05% | 89 | |
| PCMB | 2.0 | 96 | |||
| MIA | 2.0 | 91 | |||
| NaF | 2.0 | 91 | |||
| NaN₃ | 2.0 | 91 |
Ac, CH₃CO; PCMB, p-Chloromercuribenzoate; MIA, Monoiodoacetate; EDTA, Ethylenediaminetetraacetate; IAA, Iodoacetamide; NEM, N-Ethylmaleimide; SDS, Sodium dodecyl sulfate; DAC, Dimethylbenzylalkylammonium chloride.
To get a quote, contact us at info@toyobousa.com, or INQUIRY.